Advanced SQL#
Accessing SQL from a Programming Language#
- Not all queries can be expressed in SQL, since SQL does not provide the full expressive power of a general-purpose language.
不是所有的查询都能用 SQL 语言表达。 - Non-declarative actions -- such as printing a report, interacting with a user, or sending the results of a query to a graphical user interface -- cannot be done from within SQL.
用户交互是图形界面,语音、图像,数据库不具备这方面的功能。
从高级语言(如 C)访问数据库,主要是下面两种方式:
- API(Application Program Interface) -- A general-purpose program can connect to and communicate with a database server using a collection of functions.
函数库 - Embedded SQL -- provides a means by which a program can interact with a database server.
把 SQL 语句嵌入到语言内- The SQL statements are translated at compile time into function calls.
- At runtime, these function calls connect to the database using an API that provides dynamic SQL facilities.
JDBC and ODBC#
API (application-program interface) for a program to interact with a database server
Application makes calls to
- Connect with the database server
建立连接 - Send SQL commands to the database server
指令发送到服务器 - Fetch tuples of result one-by-one into program variables
拿回结果
SQL 与 C 语言存在鸿沟(如 select 得到的是集合,但是 C 语言没有这种类型)会返回指针/迭代器
- ODBC (Open Database Connectivity) works with C, C++, C#
- JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) works with Java
通过类定义,将数据库操作封装到 Java 内 - Embedded SQL in C
- SQLJ - embedded SQL in Java
- JPA(Java Persistence API) - OR mapping of Java
JDBC#
JDBC is a Java API for communicating with database systems supporting SQL.
public static void JDBCexample(String dbid, String userid, String passwd)
{
try {
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:oracle:thin:@db.yale.edu:2000:univdb", userid, passwd);
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
... Do Actual Work ...
stmt.close();
conn.close();
}
catch (SQLException sqle) {
System.out.println("SQLException : " + sqle);
}
}
- Open a connection
- Create a “statement” object
- Execute queries using the Statement object to send queries and fetch results
- Exception mechanism to handle errors
Example
- Update to database
- Execute query and fetch and print results
- Getting result fields:
- Dealing with Null values
Prepared Statement
Prepared Statement
PreparedStatement pStmt = conn.prepareStatement(
"insert into instructor values(?,?,?,?)");
pStmt.setString(1, "88877");
pStmt.setString(2, "Perry");
pStmt.setString(3, "Finance");
pStmt.setInt(4, 125000);
pStmt.executeUpdate();
pStmt.setString(1, "88878");
pStmt.executeUpdate();
setString, setInt 就是把第几个占位符设置为参数,并 executeUpdate 进行插入。
SQL Injection
Always use prepared statements when taking an input from the user and adding it to a query. NEVER create a query by concatenating strings which you get as inputs.
SQL 注入攻击。
Suppose query is constructed using select * from instructor where name = ’" + name + “ ’
Suppose the user, instead of entering a name, enters: X’ or ’Y’ = ’Y
then the resulting string of the statement becomes: select * from instructor where name = ’" + "X’ or ’Y’ = ’Y" + “’
which is: select * from instructor where name = ’X’ or ’Y’ = ’Y’
User could have even used
X’; update instructor set salary = salary + 10000;
then select * from instructor where name = ’X’; update instructor set salary = salary + 10000;
Always use prepared statements, with user inputs as parameters
Metadata Features
-
ResultSet metadata
-
Database metadata
Example
DatabaseMetaData dbmd = conn.getMetaData(); ResultSet rs = dbmd.getColumns(null, "univdb", "department", "%"); // Arguments to getColumns: Catalog, Schema-pattern, Table-pattern, // and Column-Pattern // Returns: One row for each column; row has a number of attributes // such as COLUMN_NAME, TYPE_NAME while( rs.next()) { System.out.println(rs.getString("COLUMN_NAME"), rs.getString("TYPE_NAME");
Transaction Control in JDBC
- Can turn off automatic commit on a connection
conn.setAutoCommit(false); - Transactions must then be committed or rolled back explicitly
conn.commit();orconn.rollback(); conn.setAutoCommit(true)turns on automatic commit.
所有的数据库功能都是通过 Java 封装好的类来实现的。
SQLJ#
SQLJ: embedded SQL in Java
#sql iterator deptInfoIter ( String dept name, int avgSal);
deptInfoIter iter = null;
#sql iter = { select dept_name, avg(salary) as avgSal from instructor
group by dept name };
while (iter.next()) {
String deptName = iter.dept_name();
int avgSal = iter.avgSal();
System.out.println(deptName + " " + avgSal);
}
iter.close();
#sql 标识,最后会被编译器转化为 Java 的类。
ODBC#
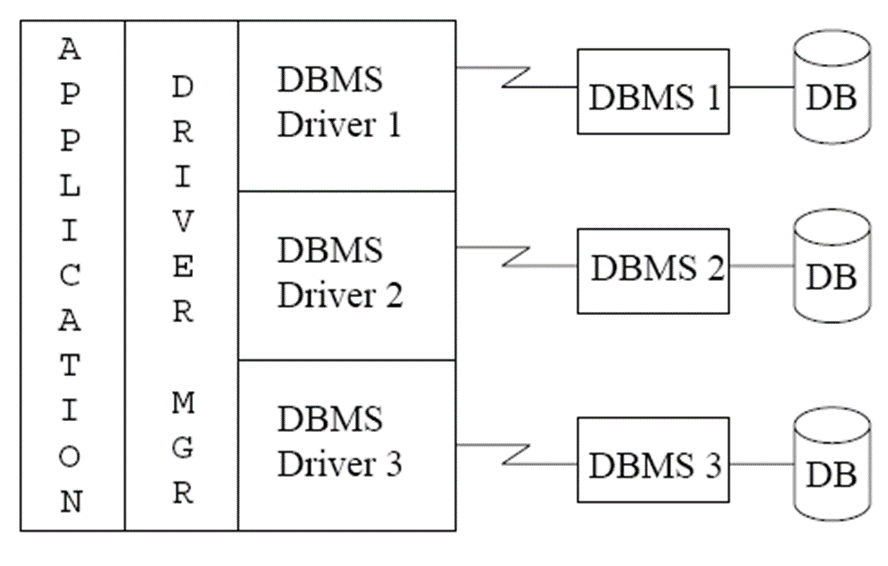
Each database system supporting ODBC provides a "driver" library that must be linked with the client program.
Example
int ODBCexample()
{
RETCODE error;
HENV env; /* environment */
HDBC conn; /* database connection */
SQLAllocEnv(&env);
SQLAllocConnect(env, &conn);
SQLConnect(conn, “db.yale.edu", SQL_NTS, "avi", SQL_NTS, "avipasswd", SQL_NTS);
{ ... Do actual work ... }
SQLDisconnect(conn);
SQLFreeConnect(conn);
SQLFreeEnv(env);
}
同一个数据库可能服务于多个用户,而且使用的编程语言可能不同,如字符串的结束标志可能也不同,因此需要用 SQL_NTS 标识。
- Program sends SQL commands to database by using
SQLExecDirect - Result tuples are fetched using
SQLFetch() SQLBindCol()binds C language variables to attributes of the query result- When a tuple is fetched, its attribute values are automatically stored in corresponding C variables.
- Arguments to SQLBindCol()
- ODBC stmt variable, attribute position in query result
- The type conversion from SQL to C.
- The address of the variable.
- For variable-length types like character arrays,
- The maximum length of the variable
- Location to store actual length when a tuple is fetched.
- Note: A negative value returned for the length field indicates null value
Example
Main body of program
char deptname[80];
float salary;
int lenOut1, lenOut2;
HSTMT stmt;
char * sqlquery = "select dept_name, sum (salary) from instructor group by dept_name";
SQLAllocStmt(conn, &stmt);
error = SQLExecDirect(stmt, sqlquery, SQL_NTS);
if (error == SQL SUCCESS) {
SQLBindCol(stmt, 1, SQL_C_CHAR, deptname , 80, &lenOut1);
SQLBindCol(stmt, 2, SQL_C_FLOAT, &salary, 0 , &lenOut2);
while (SQLFetch(stmt) == SQL_SUCCESS) {
printf (" %s %g\n", deptname, salary);
}
}
SQLFreeStmt(stmt, SQL_DROP);
char deptname[11]; 才能定义十个元组。如果结果为空,则
lenOut 为 -1.
ODBC Prepared Statements
- SQL statement prepared: compiled at the database
- To prepare a statement
SQLPrepare(stmt, <SQL String>); - To bind parameters
SQLBindParameter(stmt, <parameter#>, ... type information and value omitted for simplicity..) - To execute the statement
retcode = SQLExecute(stmt);
- To prepare a statement
- Can have placeholders: e.g.
insert into account values(?,?,?) - Repeatedly executed with actual values for the placeholders
More ODBC Features
- Metadata features
- finding all the relations in the database and
- finding the names and types of columns of a query result or a relation in the database.
- By default, each SQL statement is treated as a separate transaction that is committed automatically.
- Can turn off automatic commit on a connection
SQLSetConnectOption(conn, SQL_AUTOCOMMIT, 0)} - Transactions must then be committed or rolled back explicitly by
SQLTransact(conn, SQL_COMMIT)orSQLTransact(conn, SQL_ROLLBACK)
- Can turn off automatic commit on a connection
Embedded SQL#
A language to which SQL queries are embedded is referred to as a host language, and the SQL structures permitted in the host language comprise embedded SQL.
如把 SQL 嵌入到 C 语言,那么 C 语言是 host.
在编译前,有一个预编译器,将 SQL 语句翻译。
EXEC SQL statement is used in the host language to identify embedded SQL request to the preprocessor (in Java, # SQL { ... };)
Issues with Embedded SQL
- Mark the start point and end point of Embedded SQL
EXEC SQL <statement>; //C - Communication between database and programming language e.g. SQLCA、SQLDA
- Address the mismatching issue between SQL and host lanugage.
Handle result (set) with cursor Mapping of basic data types e.g. SQL: Date \(\rightarrow\) C: char(12)
Example
insert、delete、update、select(single record)
main( )
{ EXEC SQL INCLUDE SQLCA; //声明段开始
EXEC SQL BEGIN DECLARE SECTION;
char account_no [11]; //host variables(宿主变量)声明
char branch_name [16];
int balance;
EXEC SQL END DECLARE SECTION;//声明段结束
EXEC SQL CONNECT TO bank_db USER Adam Using Eve;
scanf (“%s %s %d”, account_no, branch_name, balance);
EXEC SQL insert into account
values (:account_no, :branch_name, :balance);
If (SQLCA.sqlcode ! = 0) printf ( “Error!\n”);
else printf (“Success!\n”);
}
两点不平衡:没有集合;没有 NULL;没有日期类型
可以在编译时进行类型检查,但 ODBC 只有在运行时才有。
- Static: Embedded SQL statements( include relation names and attribute names) are hard coded in program.
- Dynamic:Embedded SQL statements are built at run time
Procedural Constructs in SQL#
SQL provides a module language
Permits definition of procedures in SQL, with if-then-else statements, for and while loops, etc.
Stored Procedures
- Can store procedures in the database
- then execute them using the call statement
- permit external applications to operate on the database without knowing about internal details
SQL Functions#
Example

SQL 函数的返回值可以是一个 table.
Example

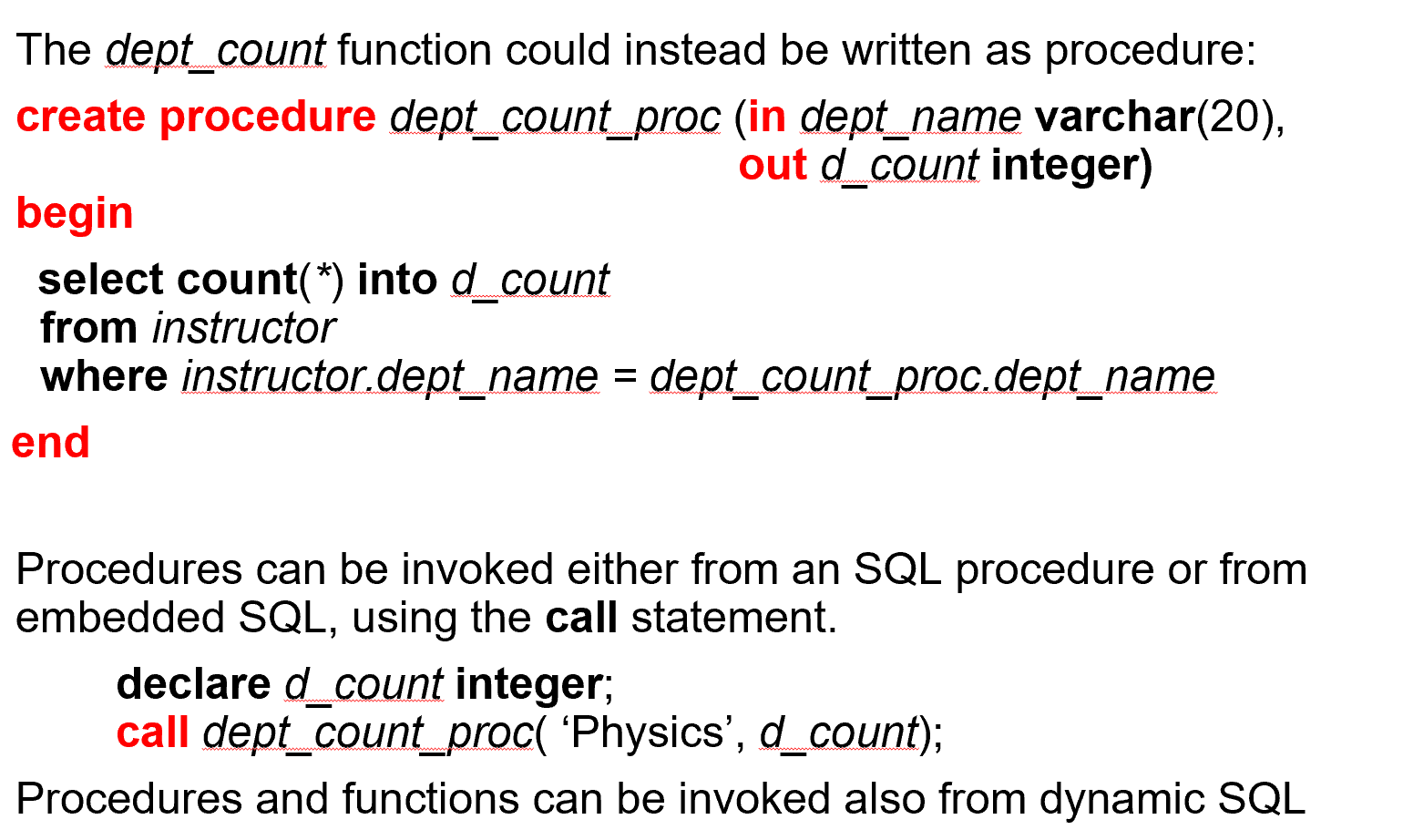
SQL Procedures#
有输入参数(in)和输出参数(out)
Example
Procedural Constructs#
Compound statement: begin ... end,
- May contain multiple SQL statements between
beginandend. -
Local variables can be declared within a compound statements
-
Whileandrepeatstatements
e.g. Forloop Permits iteration over all results of a query e.g.
r 表示返回的每一行
Example procedure

External Language Functions/Procedures#
SQL 可以访问由 C 语言定义的函数(过程)
Example
可能比较危险,放在虚拟机(Java)或者独立的线程
Triggers#
A trigger is a statement that is executed automatically by the system as a side effect of a modification to the database.
Trigger - ECA rule
- E: Event ( insert, delete ,update)
- C: Condition
- A: Action
To design a trigger mechanism, we must:
- Specify the conditions under which the trigger is to be executed.
- Specify the actions to be taken when the trigger executes.
Example
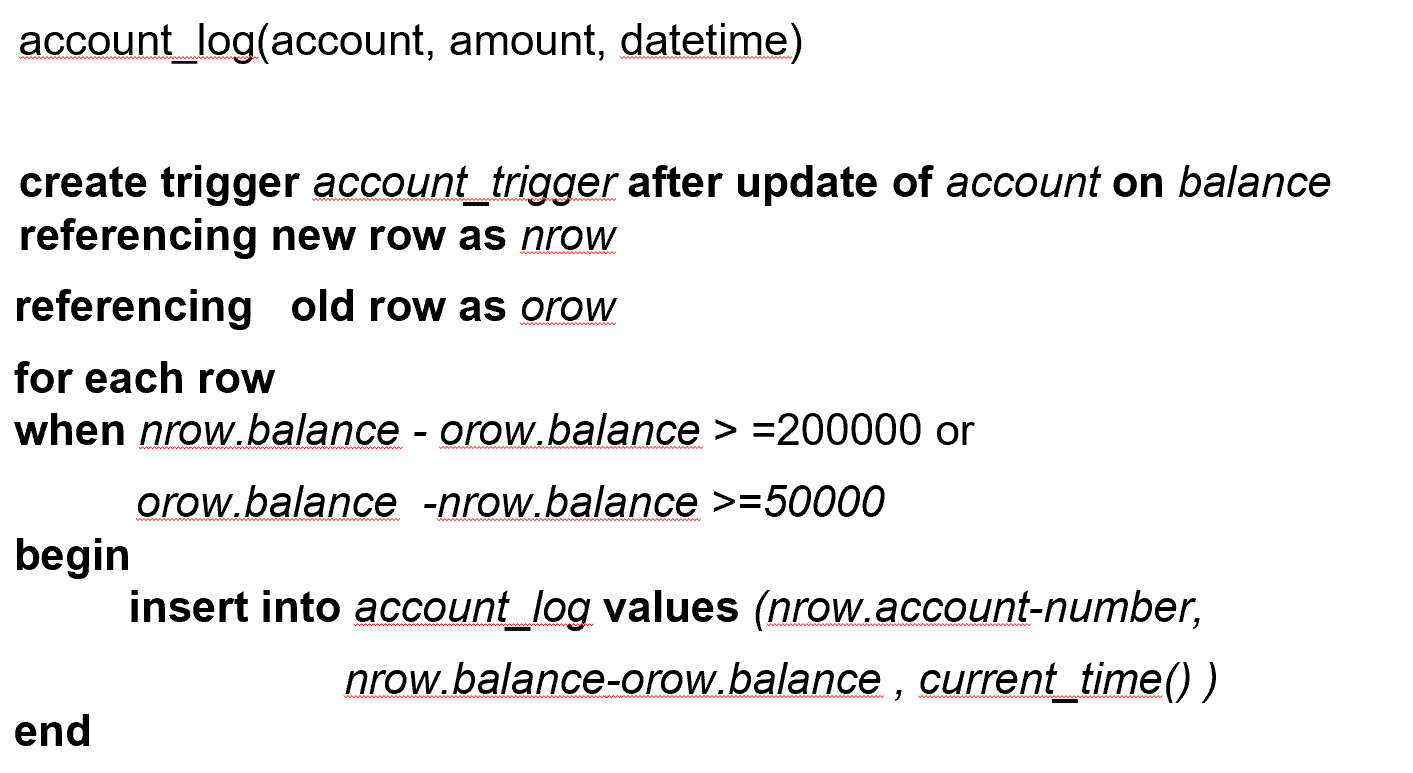
time_slot_id Example


这里 time_slot_id 不是主键,因此删除不会引起其他影响。但我们可以设计一个触发器,用来检查当前课程的 time_slot_id 是否在表内。
第二个触发器表示,time_slot_id 已经被删完了,但依然有课程在引用,就要 rollback.
- Triggering event can be insert, delete or update
- Triggers on update can be restricted to specific attributes
e.g. after(before) update of takes on grade - Values of attributes before and after an update can be referenced
- referencing old row as: for deletes and updates
- referencing new row as: for inserts and updates
Trigger to Maintain credits_earned value

如果本来挂科,或者没有成绩,更新后不再挂科而且有成绩,就把学分加上去。
要慎用触发器,用在刀刃上,可能会引发连锁反应。
Instead of executing a separate action for each affected row, a single action can be executed for all rows affected by a transaction
- Use
for each statementinstead offor each row - Use
referencing old tableorreferencing new tableto refer to temporary tables (called transition tables) containing the affected rows - Can be more efficient when dealing with SQL statements that update a large number of rows
Example

Created: 2024年3月19日 11:22:29