Lecture 3 | Introduction to SQL#
Abstract
- Data Definition
- Basic Query Structure
- Additional Basic Operations
- Set Operations
- Null Values
- Aggregate Functions
- Nested Subqueries
- Modification of the Database
Data Definition#
Domain Types in SQL#
char(n).Fixed length character string, with user-specified length n.
定长字符串. C 语言里字符串结尾有\0, 但数据库里没有,长度由定义而得。varchar(n).Variable length character strings, with user-specified maximum length n.
不定长字符串。不同的数据类型比较可能有问题(比如定长和不定长的字符串)int.Integer (a finite subset of the integers that is machine-dependent).smallint.Small integer (a machine-dependent subset of the integer domain type).numeric(p,d).Fixed point number, with user-specified precision of p digits, with d digits to the right of decimal point.
p 表示有效数字位数, d 表示小数点后多少位。 e.g.number(3,1)allows 44.5 to be store exactly, but neither 444.5 or 0.32- real, double precision. Floating point and double-precision floating point numbers, with machine-dependent precision.
float(n).Floating point number, with user-specified precision of at least n digits.
Built-in Data Types in SQL#
- date: Dates, containing a (4 digit) year, month and date
e.g. date ‘2005-7-27’ - time: Time of day, in hours, minutes and seconds. e.g. time ‘09:00:30’ time ‘09:00:30.75’
- timestamp: date plus time of day e.g. timestamp ‘2005-7-27 09:00:30.75’
- interval: period of time
e.g. interval ‘1’ day
- Subtracting a date/time/timestamp value from another gives an interval value.
- Interval values can be added to date/time/timestamp values
- built-in date, time functions:
current_date(), current_time(), year(x), month(x), day(x), hour(x), minute(x), second(x)
Create Table Construct#
An SQL relation is defined using the create table command:
- \(r\) is the name of the relation
- each \(Ai\) is an attribute name in the schema of relation \(r\)
- \(Di\) is the data type of values in the domain of attribute \(Ai\)
Integrity Constraints in Create Table
not null- primary key \((A_1,\ldots,A_n)\)
不能为空; 表内不能有相同的 keys. 否则这样的数据是插入不进去的。 - foreign key \((A_m,\ldots,A_n)\) references r
隐含:引用对应表的主键。
如果不符合完整性约束条件,插入可能会失败。
Example

可以给一个缺省值 e.g. default 0
Example

sec_id can be dropped from primary key above, to ensure a student cannot be registered for two sections of the same course in the same semester
如果引用的表中有条目被删除,可能会破坏完整性约束条件。有下面的方法:
- restrict: 如果有条目是被引用的,那么不允许删除。
- cascade: 引用的条目被删了之后,引用者也一并删除
- set null: 引用者的指针设为
null. - set default
如果引用的表中有更新,也有类似上面的四种方法。
在 create table 中定义
on delete cascade |set null |restrict |set defaulton update cascade |set null |restrict |set default
Drop and Alter Table Constructs#
- drop table student
Deletes the table and its contents
把内容和表全删了,之后不能再往表里插入。 - delete from student
Deletes all contents of table, but retains table - alter table
可以动态修改表的定义alter table r add A D- where A is the name of the attribute to be added to relation r and D is the domain of A.
- All tuples in the relation are assigned null as the value for the new attribute.
e.g.alter table student add resume varchar(256); - 还可以增加外键约束条件,也可以删掉
alter table r drop A- where A is the name of an attribute of relation r
- Dropping of attributes not supported by many databases
可以生成一个新的表,然后把除了要删的列以外的列搬移过去。
关系数据库的三层抽象
- 用户层:由 DML 定义操作, 如
select语句。 - 逻辑层:由
create table决定,我们定义了表的元素,以及各种键,构成了模式图。
Basic Query Structure#
The select Clause#
The select clause list the attributes desired in the result of a query.
SQL names are case insensitive
大小写不敏感。(属性名字、表的名字等)
- To force the elimination of duplicates, insert the keyword
distinctafter select. e.g.select distinct dept_name from instructor
可以加 all 表示不去重,加不加无所谓 - An asterisk in the select clause denotes “all attributes”
e.g.select * from instructor - The select clause can contain arithmetic expressions involving the operation, +, –, \(\div\), and /, and operating on constants or attributes of tuples.
可以有加减乘除运算 e.g.select ID, name, salary/12 from instructor
The where Clause#
The where clause specifies conditions that the result must satisfy.
Corresponds to the selection predicate of the relational algebra.
- SQL includes a
betweencomparison operator e.g.select name from instructor where salary between 90000 and 100000 - Tuple comparison
元组相等等价于各个元素都相等。 e.g.select name, course_id from instructor, teaches where (instructor.ID, dept_name) = (teaches.ID, ’Biology’);
The from clause#
The from clause lists the relations involved in the query.
Corresponds to the Cartesian product operation of the relational algebra.
Natural Join#
e.g. select * from instructor natural join teaches;
e.g. select name, course_id from instructor, teaches where instructor.ID = teaches.ID;
select name, course_id from instructor natural join teaches;
上面两条语句是等价的。
Unrelated attributes with same name which get equated incorrectly!
Example
course(course_id,title, dept_name,credits), teaches(ID, course_id,sec_id,semester, year), instructor(ID, name, dept_name,salary) 这里的 department 含义各有不同,不能直接自然连接。
可以写成 select name, title from (instructor natural join teaches)join course using(course_id); 即规定连接的属性,对应于 \(\sigma_\theta\)
Find students who takes courses across his/her department.
可写作
The Rename Operation#
The SQL allows renaming relations and attributes using the as clause.
old-name as new-name
e.g.
select distinct T. name from instructor as T, instructor as S where T.salary > S.salary and S.dept_name = ‘Comp. Sci.’
- Keyword
asis optional and may be omitted.
String Operations#
SQL includes a string-matching operator for comparisons on character strings. The operator like uses patterns that are described using two special characters.
注意单引号表示字符串。
- percent (%). The % character matches any substring.
e.g.select name from instructor where name like '%dar%';找名字里面含有dar的字符串。 - underscore (_). The _ character matches any character.
Match the string
匹配字符串 '100 %' 但是 % 符号被我们作为了通配符,这里我们需要用到转义符 \. \% 即将 % 作为正常字符匹配。
\ 也可以是一个基本符号,我们需要在后面写出 escape 表示其在这里作为转义符。类似地我们还可以将转义符定义为 #.
SQL supports a variety of string operations such as
- concatenation (using
||) - converting from upper to lower case (and vice versa)
- finding string length, extracting substrings, etc.
Ordering the Display of Tuples#
关系是无序的,但我们可能规定显示出来的顺序。
- We may specify desc for descending order or asc for ascending order, for each attribute; ascending order is the default.
e.g.order by name desc
可以排序的类型,如字符串、数字。 - Can sort on multiple attributes
e.g.order by dept_name, name先按第一个排,如果第一个元素相同再按第二个排。
The limit Clause#
The limit clause can be used to constrain the number of rows returned by the select statement.
limit clause takes one or two numeric arguments, which must both be nonnegative integer constants:
limit offset, row_countlimit row_count == limit 0, row_count
e.g. select name from instructor order by salary desc limit 3; // limit 0,3
Set Operations#
union, intersect, except是严格的集合操作,会对结果去重.union all,intersect allandexcept all. 保持多重集。
Example

Null Values#
null signifies an unknown value or that a value does not exist.
- The result of any arithmetic expression involving null is null.
e.g.5 + nullreturns null - The predicate is null can be used to check for null values.
e.g. Find all instructors whose salary is null.
select name from instructor where salary is null - Comparisons with null values return the special truth value: unknown.

- Result of select predicate is treated as false if it evaluates to unknown
Aggregate Functions#
Example
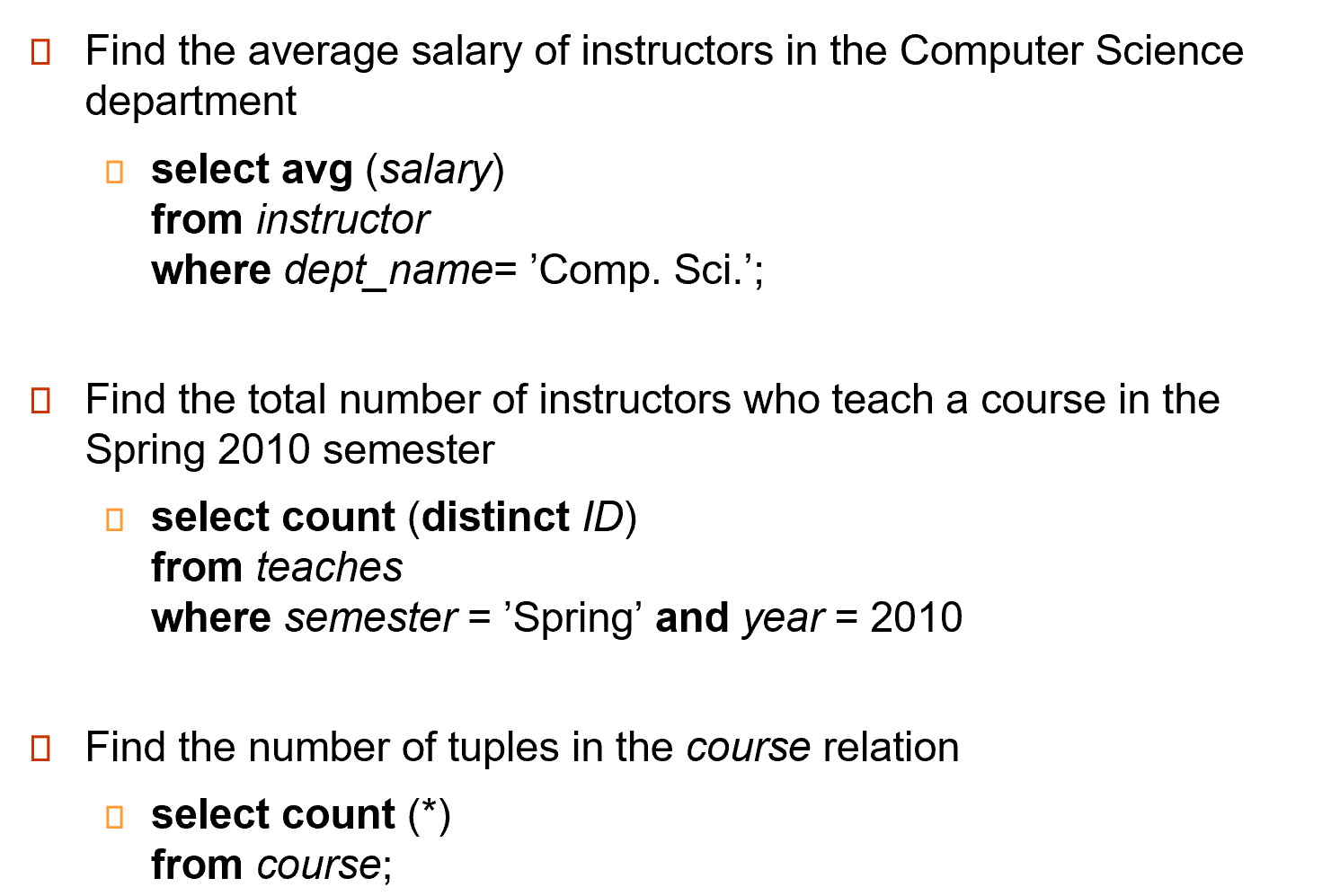
注意在 select 里出现的属性,除了统计函数以外,一定要是分组属性里出现过的。
Having Clause#
对分组后的组进行筛选。
e.g.
select dept_name, count (*) as cnt
from instructor
where salary >=100000
group by dept_name
having count (*) > 10
order by cnt;
predicates in the having clause are applied after the formation of groups whereas predicates in the where clause are applied before forming groups.
Null Values and Aggregates#
select sum (salary) from instructor
- Above statement ignores null amounts
- Result is null if there is no non-null amount
- All aggregate operations except
count(*)ignore tuples with null values on the aggregated attributes
Arithmetric expression with Aggregate functions

第二个表示重名率小于千分之一的系。
Nested Subqueries#
A subquery is a select-from-where expression that is nested within another query.
Set Membership#
in, not in
Example

除了单个元素外,元组也可以使用 in, not in
Set Comparison#
some某些成员all所有成员
Example
工资大于生物系中的某些老师的老师.
Scalar Subquery#
Scalar (标量) subquery is one which is used where a single value is expected.
Example
select name
from instructor
where salary * 10 >
(select budget from department
where department.dept_name = instructor.dept_name)
这里 dept_name 是这个表的主键,只返回一个元组,这种情况下是可以不用 some, all 的。
Runtime error if subquery returns more than one result tuple.
Test for Empty Relations#
The exists construct returns the value true if the argument subquery is nonempty.
exists r\(\Leftrightarrow r \neq \emptyset\)not exists r\(\Leftrightarrow r = \emptyset\)
Example
09FALL 开的课,而且 10SPRING 也开了课。
Example
Find all students who have taken all courses offered in the Biology department.
SQL 语句往往需要逆向考虑,即找到这样的学生,不存在他没选过的生物系的课。
Test for Absence of Duplicate Tuples#
The unique construct tests whether a subquery has any duplicate tuples in its result.
验证是否是一个集合,而非多重集。
- Evaluates to “true” on an empty set.
可以将 unique 理解为 at most once.
Example

如果不加 exist, 可能有没开过的课也被算进去。我们这里求得是恰好只开过一次的。
Example

也可以用 group by count(*) > 1 实现。
With Clause#
The with clause provides a way of defining a temporary view whose definition is available only to the query in which the with clause occurs.
构造一个临时表
Example
Find all departments with the maximum budget.
Complex Queries using With Clause

Modification of the Database#
Deletion#
Example

Insertion#
Example
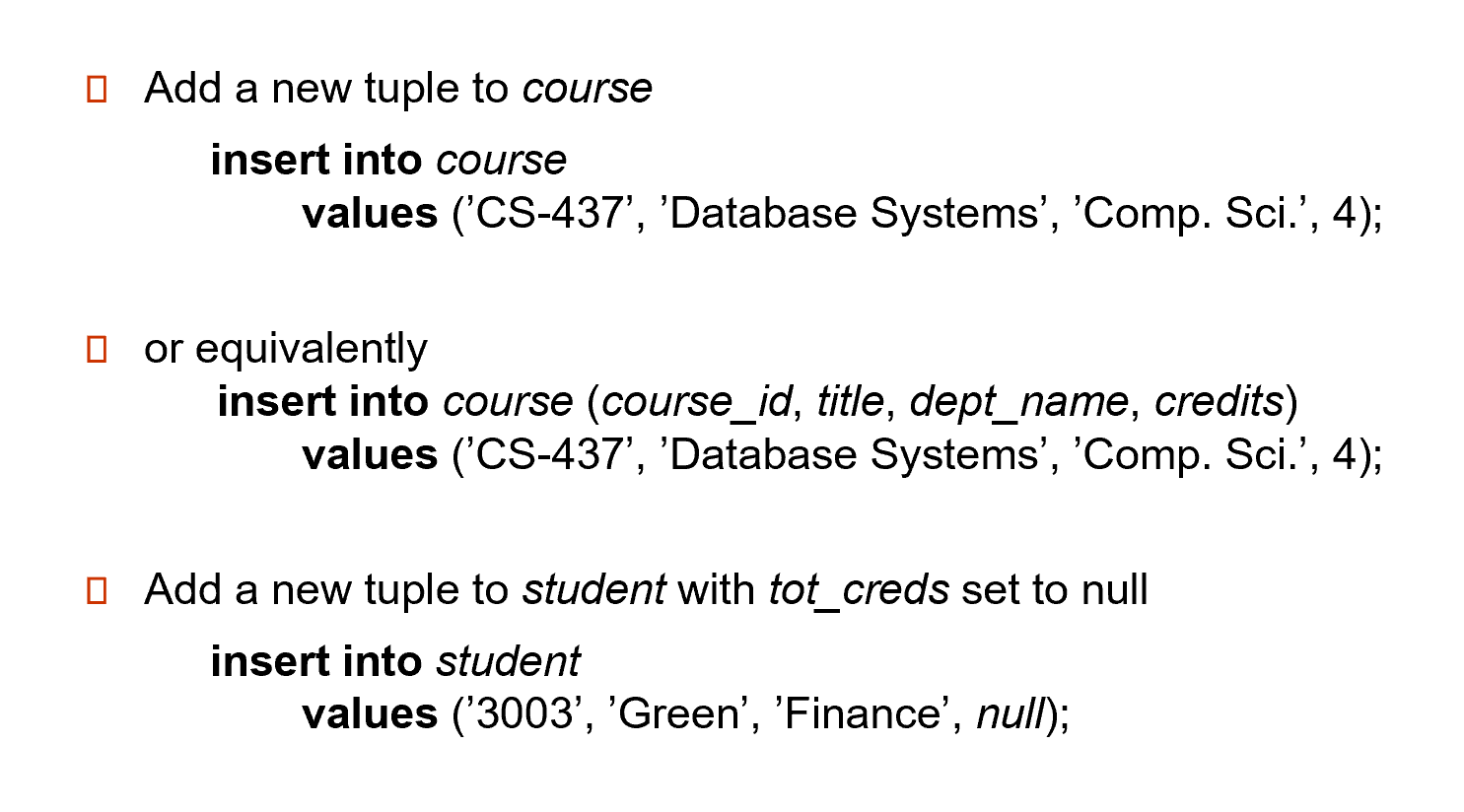
第二种写法,可以不用严格按照定义的元素顺序,只要和自己写的对应即可。
除了基本写法,我们还可以在 insert 后跟查询语句,把查询结果插入到表里去。
Example

Updates#
update ... set ...
The order is important. So it can be done better using the case statement.
Example


Created: 2024年3月19日 11:22:29