Lecture 1 | Introduction#
Abstract
- Database Systems
- Database Applications
- Purpose of Database Systems
- View of Data
- Data Models
- Database Languages
- Database Design
- Database Engine
- Database Users and Administrators
- History of Database Systems
Database Systems#
DBMS (Database Management System)

Purpose of Database Systems#
Database systems offer solutions to all the below problems.
- data redundancy (数据冗余) and inconsistency
- data isolation (数据孤立,数据孤岛)
- difficulty in accessing data
-
Integrity problems (完整性问题)
- 完整的约束条件被藏在数据和代码中,而不是显式地声明。 e.g. "account balance \(\geq\) 1"
-
Atomicity problems (原子性问题)
- Failures may leave database in an inconsistent state with partial updates carried out e.g. 从 A 账户转账到 B, 我们必须保证 A 转出 B 转入这两件事同时进行,不能被打断。
-
Concurrent access anomalies (并发访问异常)
- Uncontrolled concurrent accesses can lead to inconsistencies
Example
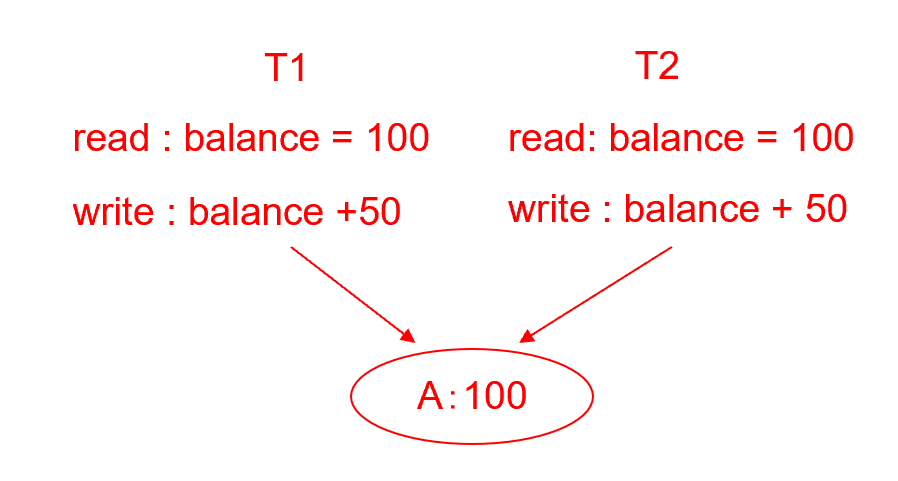
-
Security problems
- Authentication (认证), Priviledge (权限), Audit (审计)
Characteristics of Databases#
- data persistence (数据持久性)
- convenience in accessing data (数据访问便利性)
- data integrity(数据完整性)
- concurrency control for multiple user (多用户并发控制)
- failure recovery (故障恢复)
- security control (安全控制)
View of Data#
Three-level abstraction of databases

- physical level: 物理中如何保存、实现(如磁盘)
- logical level: 数据库中存储什么数据?数据之间的关系?
- view level: 不同人看到不同的他们所需要的数据
Advantages:
- Hide the complexities
- Enhance the adaptation to changes
硬件环境变化 (physical level), 可以通过调整逻辑关系和映射来适应新的硬件环境。
逻辑环境变化 (logic level), 可以通过 view 和 logic 的映射使得 view 尽量少变化。
Schema and Instance#
Similar to types and variables in programming languages.
- Schema (模式)– the logical structure of the database (physical/logical)
- Instance (实例) – the actual content of the database at a particular point in time
Data Independence#
- Physical Data Independence (物理数据独立性) – the ability to modify the physical schema without changing the logical schema
- Logical Data Independence (逻辑数据独立性) - the ability to modify the logical schema without changing the user view schema
映射修改,但不用修改 schema.
Data Models#
Data models is a collection of tools for describing data, data relationships, data semantics, data constraints.
- Relational model(关系模型)
(表格)数据库系统层面 - Entity-Relationship(实体-联系) data model
需求分析层面 - Object-based data models
- Object-oriented (面向对象数据模型)
- Object-relational (对象-关系模型模型)
- Semistructured data model (XML)(半结构化数据模型)
- Other older models:
- Network model (网状模型)
- Hierarchical model(层次模型)
Relational Model

12 tuples, 4 attributes.
Datahase Languages#
Data Definition Language (DDL, 数据定义语言)#
Example

C 语言里的 struct 经过编译后全部变为了代码(有一张符号表)但数据库里不会。
Data dictionary contains metadata (元数据,i.e. data about data)
- DDL compiler generates a set of table templates stored in a data dictionary (数据字典)
- Database schema
- Integrity constraints (完整性约束) Primary key (ID uniquely identifies instructors, 主键) Referential integrity (references constraint in SQL, 参照完整性) e.g. dept_name value in any instructor tuple must appear in department relation
- Authorization (权限)
Data Manipulation Language (DML, 数据操作语言)#
Two classes of languages
- Procedural (过程式)– user specifies what data is required and how to get those data e.g. C
- Declarative (nonprocedural,陈述式,非过程式) – user specifies what data is required without specifying how to get those data e.g. SQL
SQL is the most widely used query language
SQL Query Language#

Database Access from Application Program#
数据库必须由过程式语言编写。
Application programs generally access databases through one of * Language extensions to allow embedded SQL e.g. 通过预处理器,将 select 语句识别出来,翻译成 C 语言的函数调用。 * API (Application program interface) e.g. ODBC/JDBC which allow SQL queries to be sent to a database.
Database Design#
-
Entity Relationship Model (实体-联系模型)
一对一/一对多/多对一/多对多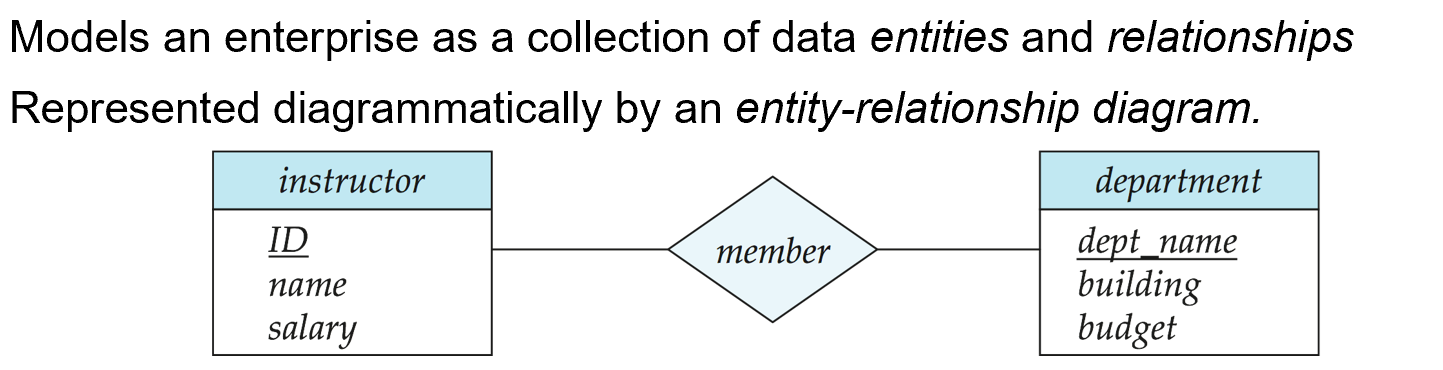
图是中立的,可以用关系数据库/面向对象数据库实现
-
Normalization Theory (规范化理论)
Formalize what designs are bad, and test for themExample
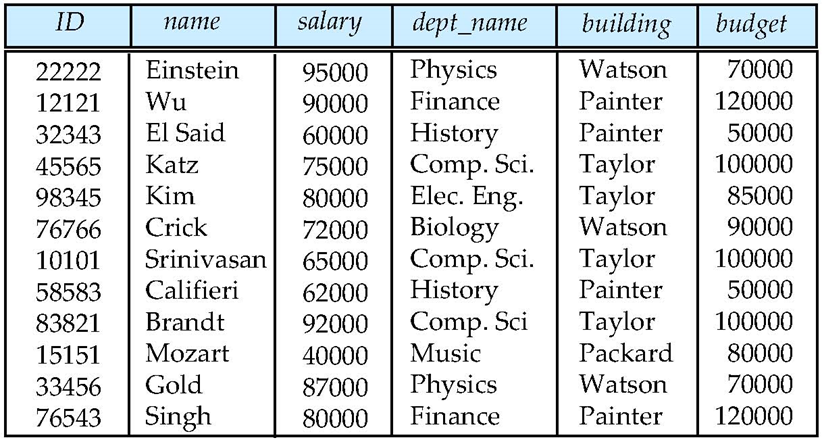
这个表存在冗余, department 有重复,应该拆分为两个表(前四列和后三列)
Database Enginee#
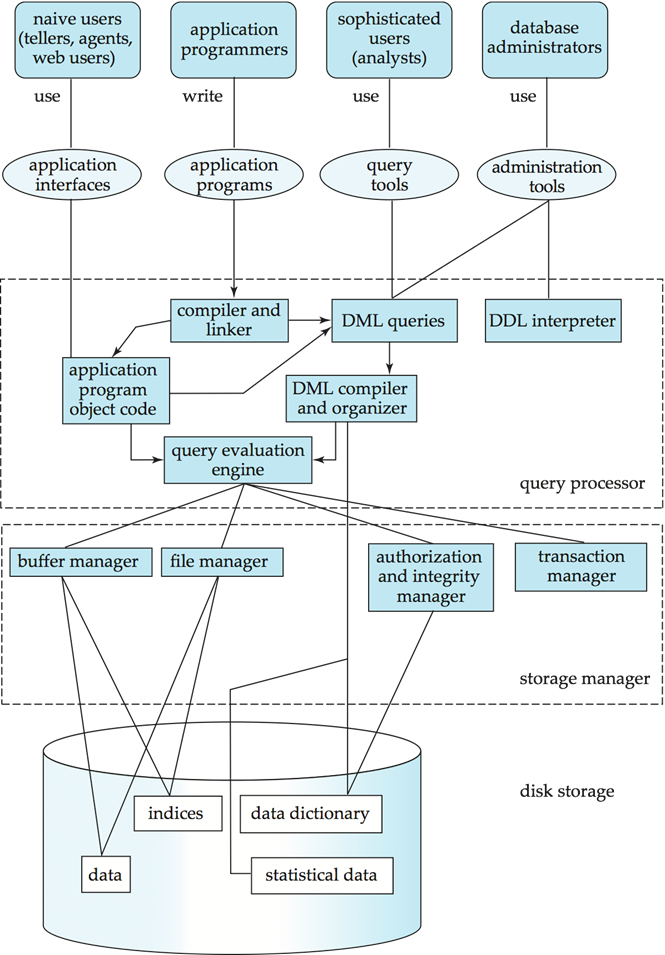
- The storage manager,
- The query processor component,
- The transaction management component.
Storage Manager#
为了数据持久化,放在硬盘里,但数据处理要进入内存,这之间存在数据鸿沟。
按块访问内存 (4k/16k), 缓冲管理。
- File manager
- Buffer manager
- Authorization and integrity manager
- Transaction manager
数据库里放的是
- data files 真正的数据
- data dictionary 放的是 metadata
- statistical data 用于数据库的查询处理
- indices
Query Processor#
The query processor components include:
- DDL interpreter -- interprets DDL statements and records the definitions in the data dictionary.
- DML compiler -- translates DML statements in a query language into an evaluation plan consisting of low-level instructions that the query evaluation engine understands.
- The DML compiler performs query optimization (查询优化); that is, it picks the lowest cost evaluation plan from among the various alternatives.
执行计划会根据统计数据的改变而改变。
- The DML compiler performs query optimization (查询优化); that is, it picks the lowest cost evaluation plan from among the various alternatives.
- Query evaluation engine -- executes low-level instructions generated by the DML compiler.
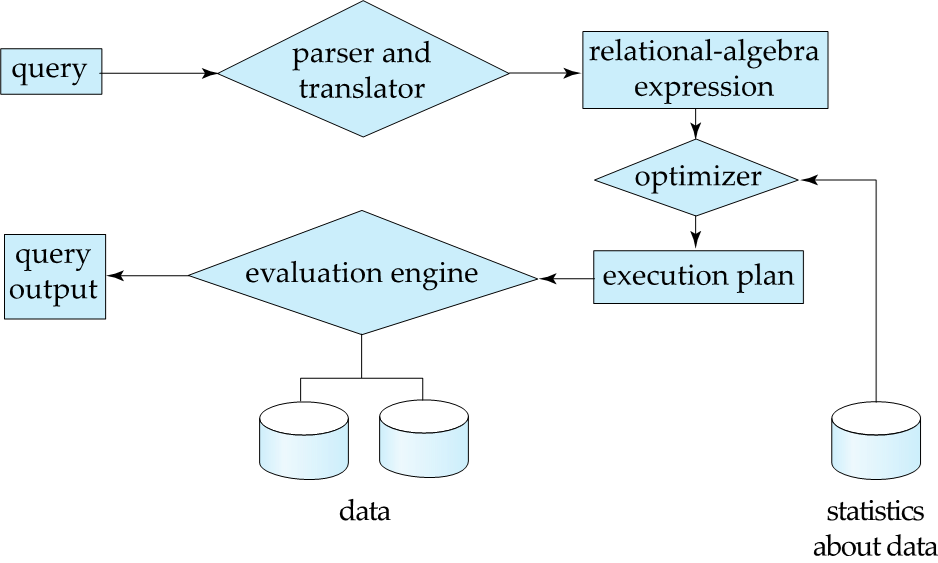
- Parsing and translation
- Optimization
- Evaluation
Transaction Management (事务管理)#
银行转账,A 转账到 B, A 余额减掉 B 余额加上。 要有隔离性,延迟写回
- Recover Manager
ensures that the database remains in a consistent (correct) state despite system failures (e.g. power failures and operating system crashes) and transaction failures.
日志,防止写回数据库时出现断电或者崩溃。 - Concurrency-control manager
controls the interaction among the concurrent transactions, to ensure the consistency of the database.
Database Users#
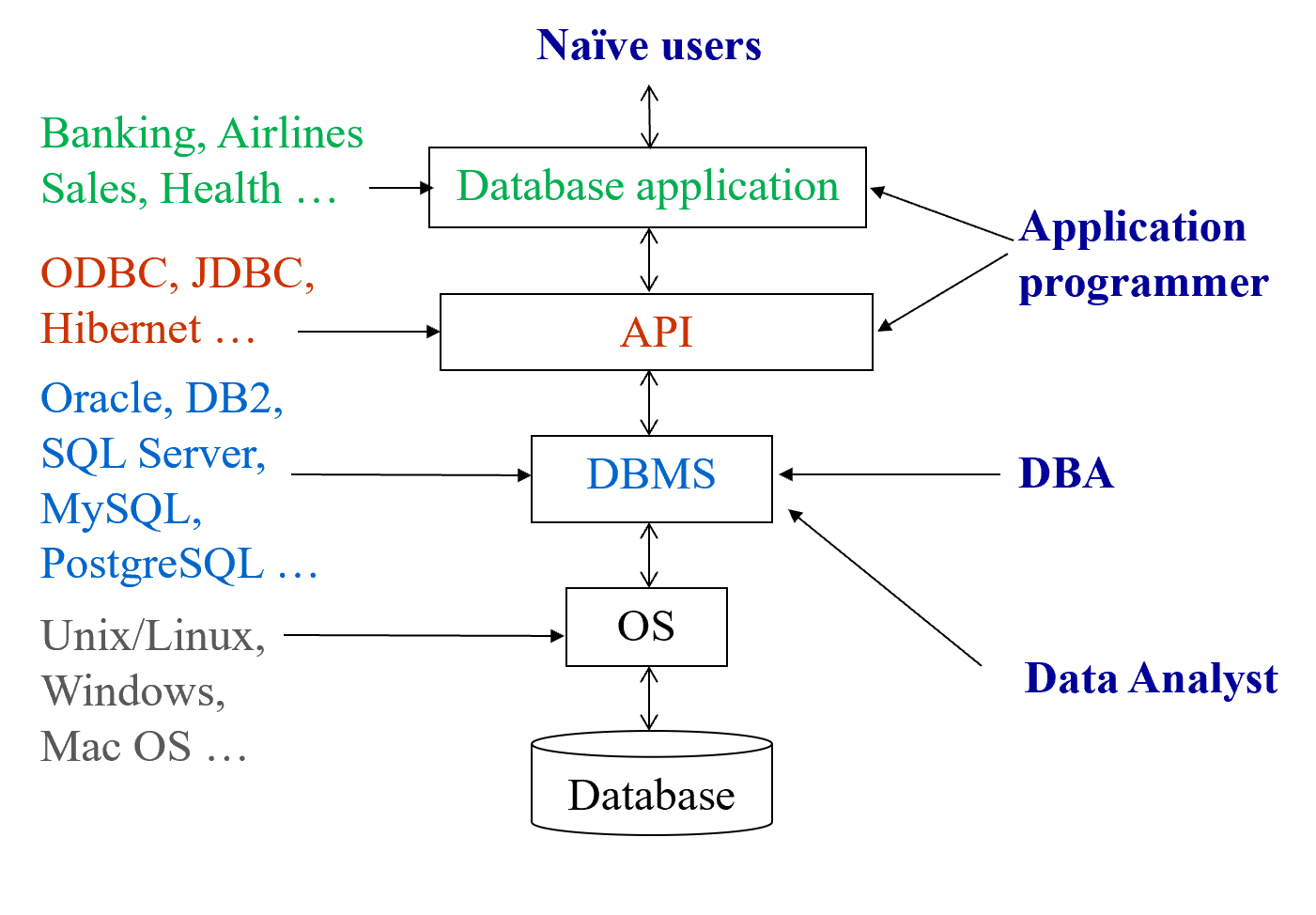
- Database Administrator (DBA)
数据库管理员,要做定义模式,数据库调谐,故障时恢复(备份)等工作。
老师:我不看好!
History#
- 1973 Turing Award: Charles W. Bachman
father of databases - 1981 Turing Award: Edgar F. Codd
- 1998 Turing Award: Jim Gray
- 2014 Turing Award: Michael Stonebraker
Created: 2024年3月19日 11:22:29